경주장
[cpp]next_permutation 정리 본문
1. 기본
// next_permutation example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation, std::sort
int main () {
int myints[] = {1,2,3};
std::sort (myints,myints+3);
std::cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n";
do {
std::cout << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n';
} while ( std::next_permutation(myints,myints+3) );
std::cout << "After loop: " << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n';
return 0;2. 벡터
// next_permutation vector example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main () {
vector<int> myints = {1,2,3};
cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n";
do {
cout << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n';
} while ( next_permutation(myints.begin(),myints.end()) );
cout << "After loop: " << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n';
return 0;
}vector는 begin( )과 end( )를 통해 permutation loop 가능
실행 결과
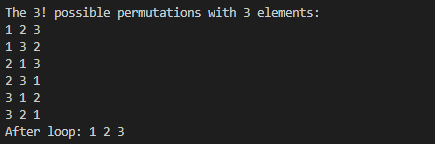
3. string
// next_permutation vector example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main () {
string s = "abc";
cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n";
do {
cout<<s<<endl;
} while ( next_permutation(s.begin(),s.end()) );
cout<<s<<endl;
return 0;
}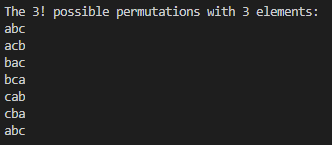
역시 가능
4. note
next_permutation( ) 활용 전 대상 배열, vector, array를 꼭 sort해주어야 한다.
사전배열기반(lexicographical) 의 loop를 지원하기 때문이다.
이에 중복이 있는 경우는 index permutation방식으로 응용하여 원하는 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
// next_permutation example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation, std::sort
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main () {
vector<int> v = {1,1,2,2};
cout << "fail :( \n";
do {
cout << v[0] << ' ' << v[1] << ' ' << v[2] << ' ' << v[3] <<endl;
} while ( next_permutation(v.begin(),v.end()) );
return 0;
}
sort되어 있음에도 4! (24)개의 모든 permutation을 출력 하지 못했다.
// next_permutation example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation, std::sort
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main () {
vector<int> v = {1,1,2,2};
vector<int> ind = {0,1,2,3};
cout << "success :) \n";
do {
cout << v[ind[0]] << ' ' << v[ind[1]] << ' ' << v[ind[2]] << ' ' << v[ind[3]] <<endl;
} while ( next_permutation(ind.begin(),ind.end()) );
return 0;
}보조 vector - ind를 통해 24개의 순열이 모두 출력가능하다.
5. 조합
어려운 문제일 수록 단순히 next_permutation( )을 순열로 활용할 각을 주지 않고
ind = [0,0,0, ... , 0, 1, ... ,1]을 동원하여 조합으로 활용하는 테크닉이 요구 되는 듯 하다.
ind의 길이 n 1의 개수 r의 경우 nCr을 가능하게 해주는 보조 index vector로 활용된다.
let vector<int> v = {5,4,3,2,1};
goal is to print all 10 cobination of choosing 3 elements of vector v.
// next_permutation example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation, std::sort
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main () {
vector<int> v = {5,4,3,2,1};
vector<int> ind = {0,0,1,1,1};
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
do {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++)
if(ind[i])
cout<< v[i] <<" ";
cout<<endl;
} while ( next_permutation(ind.begin(),ind.end()) );
return 0;
}

결과
만약 1 2 3 / 1 2 4 / 1 2 5의 순서로 loop하고 싶다면
ind 를 {1,1,1,0,0} 로 하고 next_permutation대신 prev_permutation을 활용하면 된다.
